Laryngitis |
|
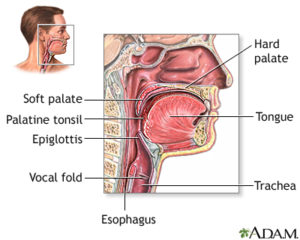
DefinitionLaryngitis is swelling and irritation (inflammation) of the voice box (larynx). The problem is most often associated with hoarseness or loss of voice. Alternative NamesHoarseness CausesThe voice box (larynx) is located at the top of the airway to the lungs (trachea). The larynx contains the vocal cords. When the vocal cords become inflamed or infected, they swell. This can cause hoarseness. Sometimes the airway can get blocked. The most common form of laryngitis is an infection caused by a virus. It may also be caused by:
Laryngitis often occurs with an upper respiratory infection, which is typically caused by a virus. Several forms of laryngitis occur in children that can lead to dangerous or fatal respiratory blockage. These forms include:
SymptomsSymptoms may include:
Exams and TestsA physical exam can find whether hoarseness is caused by a respiratory tract infection. People with hoarseness that lasts more than a month (especially smokers) will need to see an ear, nose, and throat doctor (otolaryngologist). Tests of the throat and upper airway will be done. TreatmentCommon laryngitis is often caused by a virus, so antibiotics likely will not help. Your health care provider will make this decision. Resting your voice helps to reduce inflammation of the vocal cords. A humidifier may soothe the scratchy feeling that comes with laryngitis. Decongestants and pain medicines may relieve the symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Outlook (Prognosis)Laryngitis that is not caused by a serious condition often gets better on its own. Possible ComplicationsIn rare cases, severe respiratory distress develops. This requires immediate medical attention. When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalCall your health care provider if:
PreventionTo prevent getting laryngitis:
ReferencesAllen CT, Merati AL. Acute and chronic laryngitis. In: Flint PW, Haughey BH, Lund LJ, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2015:chap 62. Schwartz SR, Cohen SM, Dailey SH, et al. Clinical practice guideline: hoarseness (dysphonia). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;141(3 Suppl 2):S1-S31. PMID: 19729111 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19729111. |